In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge. One crucial strategy for achieving this is through effective Knowledge Management. This involves capturing, storing, sharing, and effectively using organizational knowledge to improve decision-making, enhance innovation, and boost overall performance. Understanding the nuances of Knowledge Management is therefore paramount for any organization striving for sustained success and growth in the modern era.
What is Knowledge Management?
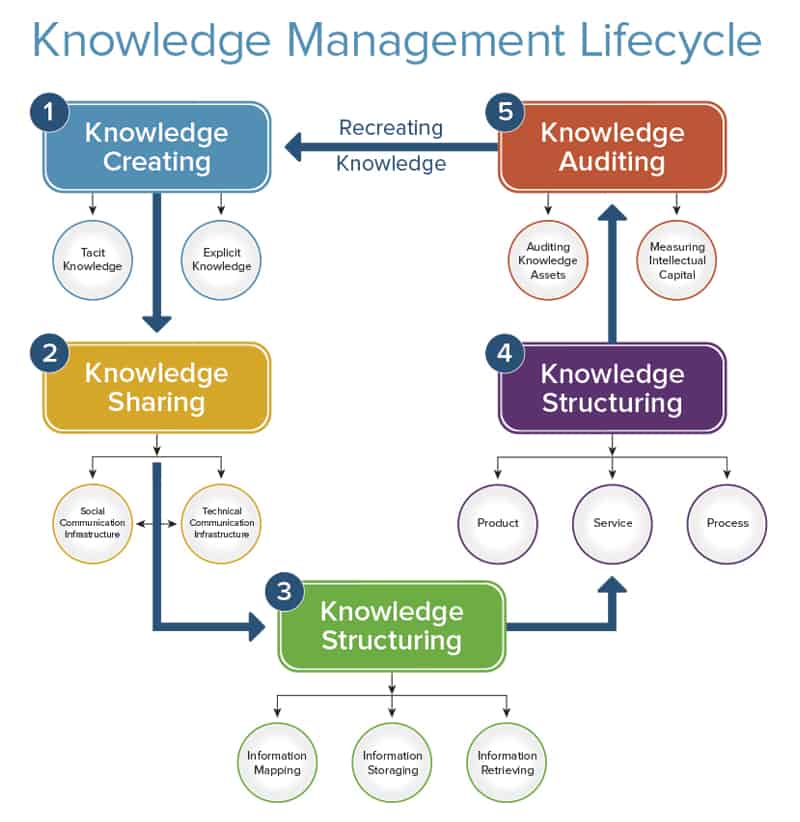
Knowledge Management (KM) is more than just storing information; it’s about creating a system where knowledge is actively used to improve business processes. It encompasses the strategies and practices used to identify, create, represent, distribute, and enable adoption of insights and experiences. This includes both explicit knowledge (documented information) and tacit knowledge (know-how and expertise residing in individuals’ minds).
Key Components of Knowledge Management
- Knowledge Creation: Generating new knowledge through research, experimentation, and collaboration.
- Knowledge Capture: Identifying and documenting existing knowledge within the organization.
- Knowledge Storage: Organizing and storing knowledge in a readily accessible format.
- Knowledge Sharing: Facilitating the dissemination of knowledge throughout the organization.
- Knowledge Application: Using knowledge to improve decision-making and problem-solving.
Benefits of Implementing Knowledge Management
Implementing a robust KM system can yield significant benefits for organizations of all sizes. These benefits include:
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to relevant knowledge enables better-informed decisions.
- Enhanced Innovation: Sharing knowledge fosters creativity and innovation.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and reduced duplication of effort.
- Reduced Risk: Learning from past mistakes and avoiding similar errors.
- Improved Customer Service: Empowered employees can provide better customer support.
Effective knowledge transfer is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage. Consider the scenario where a senior employee with decades of experience is nearing retirement. Without a proper KM system in place, their valuable tacit knowledge could be lost, potentially impacting the organization’s ability to perform certain tasks or solve specific problems. A well-designed KM strategy ensures that this knowledge is captured and shared, safeguarding the organization’s intellectual assets.
Knowledge Management Tools and Technologies
A variety of tools and technologies can support Knowledge Management initiatives. These include:
- Knowledge Bases: Centralized repositories for storing and organizing knowledge.
- Collaboration Platforms: Tools for facilitating communication and knowledge sharing.
- Document Management Systems: Systems for managing and controlling documents.
- Search Engines: Tools for quickly finding relevant information.
- Expert Systems: Systems that capture and codify the knowledge of experts.
FAQ about Knowledge Management
What is the difference between data, information, and knowledge?
Data is raw, unorganized facts. Information is data that has been processed and given context. Knowledge is information that has been understood and applied.
How do I get started with Knowledge Management?
Start by assessing your organization’s current knowledge management practices. Identify areas where knowledge is not being effectively captured or shared. Develop a KM strategy that aligns with your business goals. Choose the right tools and technologies to support your KM initiatives.
How do I measure the success of my Knowledge Management program?
Track key metrics such as improved decision-making, increased innovation, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Implementing Knowledge Management
Implementing KM can be challenging. Common obstacles include:
- Lack of buy-in from leadership: KM requires commitment from all levels of the organization.
- Resistance to change: Employees may be reluctant to share their knowledge.
- Lack of resources: Implementing KM requires investment in tools, technologies, and training.
- Difficulty in measuring ROI: It can be challenging to quantify the benefits of KM.
Ultimately, successful Knowledge Management hinges on creating a culture of learning and collaboration. By fostering an environment where knowledge is valued and shared, organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve sustainable success.