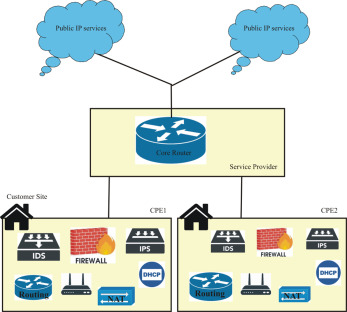
In the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunications and networking‚ understanding the various components and technologies is crucial. One such component‚ often overlooked but essential‚ is Customer Premises Equipment‚ or CPE. CPE refers to the hardware and software located at the customer’s location‚ enabling them to access services provided by a service provider. This equipment acts as the interface between the provider’s network and the customer’s internal network‚ playing a vital role in delivering internet‚ television‚ and phone services. Let’s delve deeper into the definition‚ types‚ and importance of CPE.
Understanding the Definition of CPE
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) is any equipment located on the customer’s property and connected to a service provider’s network. This equipment can range from simple devices like modems and routers to more complex systems like PBX systems and set-top boxes. The key characteristic is its location: it resides at the customer’s site‚ not within the service provider’s infrastructure.
The term “customer premises” is broad and can include homes‚ offices‚ and other business locations. The equipment is owned by either the customer or the service provider‚ depending on the agreement between them.
Types of CPE
CPE encompasses a wide variety of devices‚ each serving a specific purpose. Here are some common examples:
- Modems: Convert digital signals from the service provider’s network into a format that can be used by the customer’s devices.
- Routers: Distribute internet access to multiple devices within the customer’s network.
- Set-Top Boxes (STBs): Decode television signals for viewing on a television.
- PBX Systems: Manage phone calls and internal communications for businesses.
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs): Provide Wi-Fi connectivity to devices within the customer’s premises.
- Optical Network Terminals (ONTs): Used in fiber optic networks to convert optical signals to electrical signals.
The Importance of CPE
CPE plays a critical role in delivering services to customers. It acts as the bridge between the service provider’s network and the customer’s devices. Without CPE‚ customers would not be able to access the services they subscribe to‚ such as internet‚ television‚ and phone. Furthermore‚ CPE often provides security features like firewalls and encryption‚ protecting the customer’s network from external threats.
The quality and performance of CPE can significantly impact the customer’s experience. A poorly performing modem or router can lead to slow internet speeds and dropped connections. Therefore‚ selecting and maintaining appropriate CPE is essential for both customers and service providers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing CPE
Selecting the right CPE is crucial for optimal performance and reliability. Here are some factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure the CPE is compatible with the service provider’s network and the customer’s devices.
- Performance: Choose CPE that can handle the customer’s bandwidth requirements.
- Security: Select CPE with robust security features to protect the customer’s network.
- Reliability: Opt for CPE from reputable manufacturers known for their reliability.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the CPE and its long-term maintenance expenses.
Managed vs. Unmanaged CPE
CPE can be either managed or unmanaged. Managed CPE is typically provided and maintained by the service provider‚ while unmanaged CPE is purchased and maintained by the customer. Managed CPE offers the advantage of professional support and maintenance‚ but it may come with higher monthly fees. Unmanaged CPE provides more control over the equipment but requires the customer to handle any technical issues.
Future Trends in CPE
The CPE landscape is constantly evolving‚ driven by technological advancements and changing customer needs. Some key trends include:
- Increased bandwidth demands: As customers consume more bandwidth-intensive applications‚ CPE must be able to handle higher data rates.
- The rise of cloud-based services: CPE is increasingly being integrated with cloud-based services‚ providing new features and capabilities.
- The growing importance of security: As cyber threats become more sophisticated‚ CPE must provide robust security features to protect customer networks.
Factoid: Many modern CPE devices‚ such as routers‚ now include built-in VPN (Virtual Private Network) capabilities for enhanced security and privacy.
FAQ: Customer Premises Equipment
What does CPE stand for?
CPE stands for Customer Premises Equipment.
Who owns the CPE?
The ownership of CPE can vary. It can be owned by either the customer or the service provider‚ depending on the agreement between them.
What are some examples of CPE?
Examples of CPE include modems‚ routers‚ set-top boxes‚ PBX systems‚ and wireless access points.
Why is CPE important?
CPE is important because it enables customers to access services provided by a service provider‚ such as internet‚ television‚ and phone.
What is the difference between managed and unmanaged CPE?
Managed CPE is typically provided and maintained by the service provider‚ while unmanaged CPE is purchased and maintained by the customer.