In today’s interconnected world, computer networks are the backbone of communication and information sharing. They enable us to connect with individuals across the globe, access vast repositories of data, and collaborate on projects regardless of geographical location. Understanding the fundamentals of computer networks, their features, and their diverse applications is crucial for navigating the digital landscape. This article provides a detailed exploration of computer networks, delving into their definition, key characteristics, and widespread uses.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a collection of two or more computers or other computing devices that are interconnected and can communicate with each other. This connection allows them to share resources, such as files, printers, and internet access. Networks can range in size from small home networks to massive global networks like the internet.
Key Features of Computer Networks
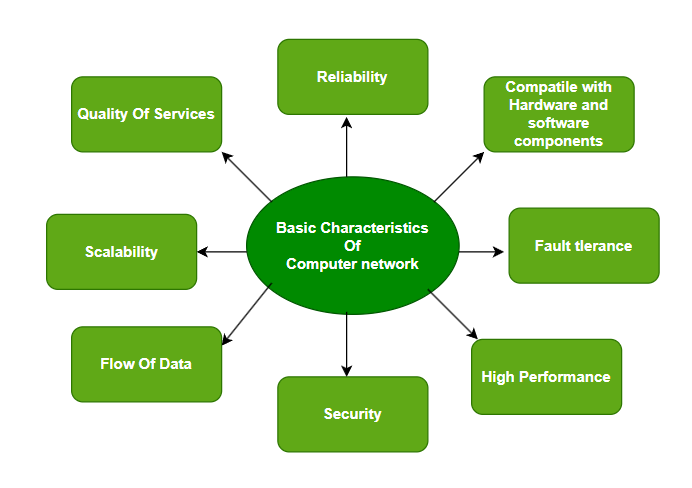
Computer networks offer a wide range of benefits and are characterized by several key features:
- Resource Sharing: Networks allow users to share resources such as printers, scanners, and storage devices, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Communication: They facilitate communication between users through email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and other communication tools.
- Data Sharing: Networks enable the sharing of files, documents, and other data between users, promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Centralized Management: Networks can be centrally managed, allowing administrators to control access, security, and other network settings;
- Increased Reliability: If one computer fails in a network, other computers can still function, ensuring business continuity.
Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks can be classified based on their size, geographical scope, and architecture. Some common types of networks include:
- Local Area Network (LAN): A network that connects computers in a small area, such as a home, office, or school.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A network that connects computers over a large geographical area, such as a city, country, or the world. The internet is the largest WAN.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A network that connects computers within a metropolitan area, such as a city or a large town.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): A network that connects devices within a person’s immediate vicinity, such as a Bluetooth headset connected to a smartphone.
Uses of Computer Networks
Computer networks are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Business: Networks are used for communication, collaboration, data sharing, and access to business applications.
- Education: Networks are used for online learning, research, and communication between students and teachers.
- Healthcare: Networks are used for electronic health records, telemedicine, and communication between healthcare providers.
- Entertainment: Networks are used for online gaming, streaming video, and social networking.
- Government: Networks are used for communication, data sharing, and providing government services online.
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of computers and other devices in a network; Common network topologies include:
- Bus Topology: All devices are connected to a single cable.
- Star Topology: All devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
- Ring Topology: All devices are connected in a closed loop.
- Mesh Topology: Each device is connected to multiple other devices.
The Importance of Network Security
Network security is critical for protecting data and resources from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Organizations must implement security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls to protect their networks.
Future Trends in Computer Networking
The field of computer networking is constantly evolving. Some emerging trends include:
- 5G Technology: Provides faster speeds and lower latency for mobile devices.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Allows for centralized management and control of network resources.
- Cloud Networking: Enables organizations to build and manage networks in the cloud.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connects billions of devices to the internet, creating new opportunities and challenges for networking.
Factoid: The TCP/IP protocol suite, which is the foundation of the internet, was developed in the 1970s.
FAQ ― Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN?
A LAN (Local Area Network) connects devices in a small area, like a home or office, while a WAN (Wide Area Network) connects devices over a large geographical area, like a city or country.
What is network security?
Network security refers to the measures taken to protect a network and its resources from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
What is a network topology?
A network topology is the physical or logical arrangement of devices in a network.
Why are computer networks important?
Computer networks are essential for communication, collaboration, resource sharing, and access to information in today’s digital world.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and network connectivity that enable these objects to collect and exchange data.
Choosing the Right Network for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate network type and configuration depends heavily on your specific requirements. Consider factors such as the number of devices, the geographical area to be covered, the desired level of security, and your budget. A small home office might only need a simple LAN, while a large corporation will likely require a complex WAN with robust security measures.
Understanding Network Protocols
Network protocols are sets of rules that govern how data is transmitted over a network. These protocols ensure that data is sent and received correctly, and that different devices can communicate with each other. Some common network protocols include:
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The foundation of the internet, used for reliable data transmission.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring web pages and other content over the internet.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files between computers.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending email.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Translates domain names (like google.com) into IP addresses.
Troubleshooting Common Network Problems
Even with the best planning, network problems can arise. Common issues include slow speeds, connectivity problems, and security breaches. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps:
- Check Cables and Connections: Ensure all cables are properly connected and that there are no loose connections.
- Restart Devices: Rebooting your router, modem, and computers can often resolve temporary issues.
- Run Network Diagnostics: Use built-in network diagnostic tools to identify potential problems.
- Update Drivers: Ensure your network adapter drivers are up to date.
- Check Firewall Settings: Make sure your firewall is not blocking necessary network traffic.
The Role of Network Administrators
Network administrators are responsible for designing, implementing, and managing computer networks. They ensure that networks are secure, reliable, and efficient. Their duties include:
- Installing and configuring network hardware and software.
- Monitoring network performance and troubleshooting problems.
- Implementing security measures to protect the network from threats.
- Managing user accounts and access permissions.
- Planning for network upgrades and expansions.
Factoid: The number of devices connected to the internet is expected to reach over 75 billion by 2025.
The Impact of Computer Networks on Society
Computer networks have revolutionized the way we live, work, and communicate. They have enabled globalization, facilitated access to information, and transformed industries across the board. From online banking to social media, computer networks are an integral part of modern society.
Computer networks are essential infrastructure for modern society. Understanding their definition, features, uses, and the technologies that underpin them is crucial for anyone working in the technology field or simply navigating the digital world. As technology continues to advance, computer networks will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in shaping our future.