Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) are collaborative ventures between governmental bodies and private sector companies. These partnerships are designed to leverage the strengths of both sectors to deliver public services or infrastructure projects more efficiently and effectively. By sharing resources, expertise, and risks, PPPs aim to achieve better outcomes than either sector could achieve independently; This approach allows governments to benefit from private sector innovation and capital while maintaining control over essential public services.
Defining Public-Private Partnerships
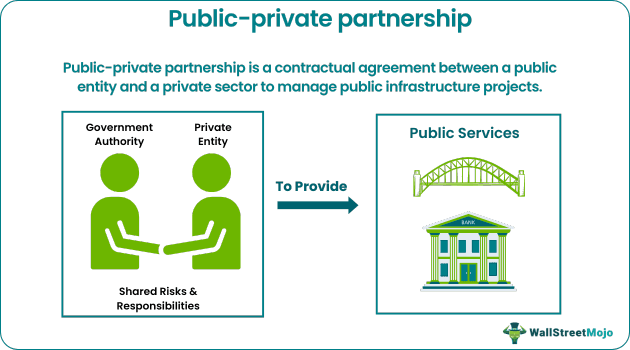
At its core, a Public-Private Partnership is a contractual agreement between a public agency (federal, state, or local) and a private sector entity. This agreement outlines the responsibilities, risks, and rewards associated with a specific project or service. The private sector typically provides financing, design, construction, operation, and maintenance, while the public sector provides oversight, regulatory approvals, and often, some form of financial contribution or guarantee.
- Shared Risk: Risks are allocated to the party best equipped to manage them.
- Long-Term Contracts: PPPs often involve long-term agreements, spanning decades.
- Performance-Based Payments: Payments to the private partner are often tied to performance metrics.
The Development of PPPs
The concept of PPPs has evolved significantly over time. Initially focused on infrastructure projects like toll roads and bridges, PPPs have expanded to encompass a wide range of sectors, including healthcare, education, and public transportation. The increasing complexity of public infrastructure needs and the growing demand for efficient public services have fueled the growth and adoption of PPPs globally. Different models of PPPs have emerged, each tailored to specific project requirements and regional contexts.
Historical Context
Early forms of PPPs can be traced back centuries, but the modern resurgence began in the late 20th century, driven by factors like fiscal constraints and a desire for improved service delivery. Countries like the UK and Australia were early adopters, pioneering innovative PPP models that have since been adapted and implemented worldwide.
Benefits of Public-Private Partnerships
PPPs offer several potential advantages:
- Improved Efficiency: Private sector expertise can lead to more efficient project design and execution.
- Reduced Costs: Private sector innovation and risk management can lower overall project costs.
- Faster Project Delivery: PPPs can often accelerate project timelines compared to traditional public procurement.
- Access to Private Capital: PPPs allow governments to leverage private sector investment to fund public projects.
- Innovation: Private partners are incentivized to introduce innovative solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
While PPPs offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges:
- Complexity: PPPs are complex legal and financial arrangements that require careful structuring.
- Transparency: Ensuring transparency and accountability in PPP projects is crucial to maintain public trust.
- Risk Allocation: Properly allocating risks between the public and private sectors is essential for project success.
- Long-Term Commitment: PPPs require a long-term commitment from both the public and private partners.
- Potential for Conflicts: Disagreements between the public and private partners can arise and need to be addressed effectively.
Factoid: A common criticism of PPPs is the potential for private companies to prioritize profit over public interest. Strong regulatory oversight is essential to mitigate this risk.
Examples of Successful PPPs
Numerous successful PPP projects demonstrate the potential of this approach. Examples include:
- Highway Construction: Toll roads and highways built and maintained through PPP agreements.
- Water Treatment Plants: Privately financed and operated water treatment facilities.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals built and managed under PPP arrangements.
- Schools and Educational Institutions: Schools and universities developed and maintained through PPPs.
Case Study: A Successful PPP Project
Consider the example of [Insert a specific example of a successful PPP project here, with details about the project, the partners involved, and the outcomes achieved. Research a real-world example to make this section more compelling and informative]. This project demonstrates the potential of PPPs to deliver significant benefits to the public.
FAQ: Public-Private Partnerships
What is the main advantage of a PPP?
The main advantage is the leveraging of private sector expertise and capital to deliver public services more efficiently and effectively.
How are risks allocated in a PPP?
Risks are typically allocated to the party best equipped to manage them.
Who benefits from a PPP?
Ideally, both the public and private sectors benefit, as well as the end-users of the services provided.
Are PPPs always successful?
No, PPPs are not always successful. Careful planning, risk allocation, and strong regulatory oversight are crucial for success.
What sectors commonly use PPPs?
Common sectors include infrastructure, healthcare, education, and transportation.