In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, operational efficiency is paramount. Companies are constantly seeking ways to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a powerful tool to achieve these goals, offering a comprehensive solution that integrates various aspects of the production cycle. This article explores how ERP systems contribute to enhanced efficiency in production processes, from raw material management to finished goods delivery.
Understanding ERP Systems and Production Efficiency
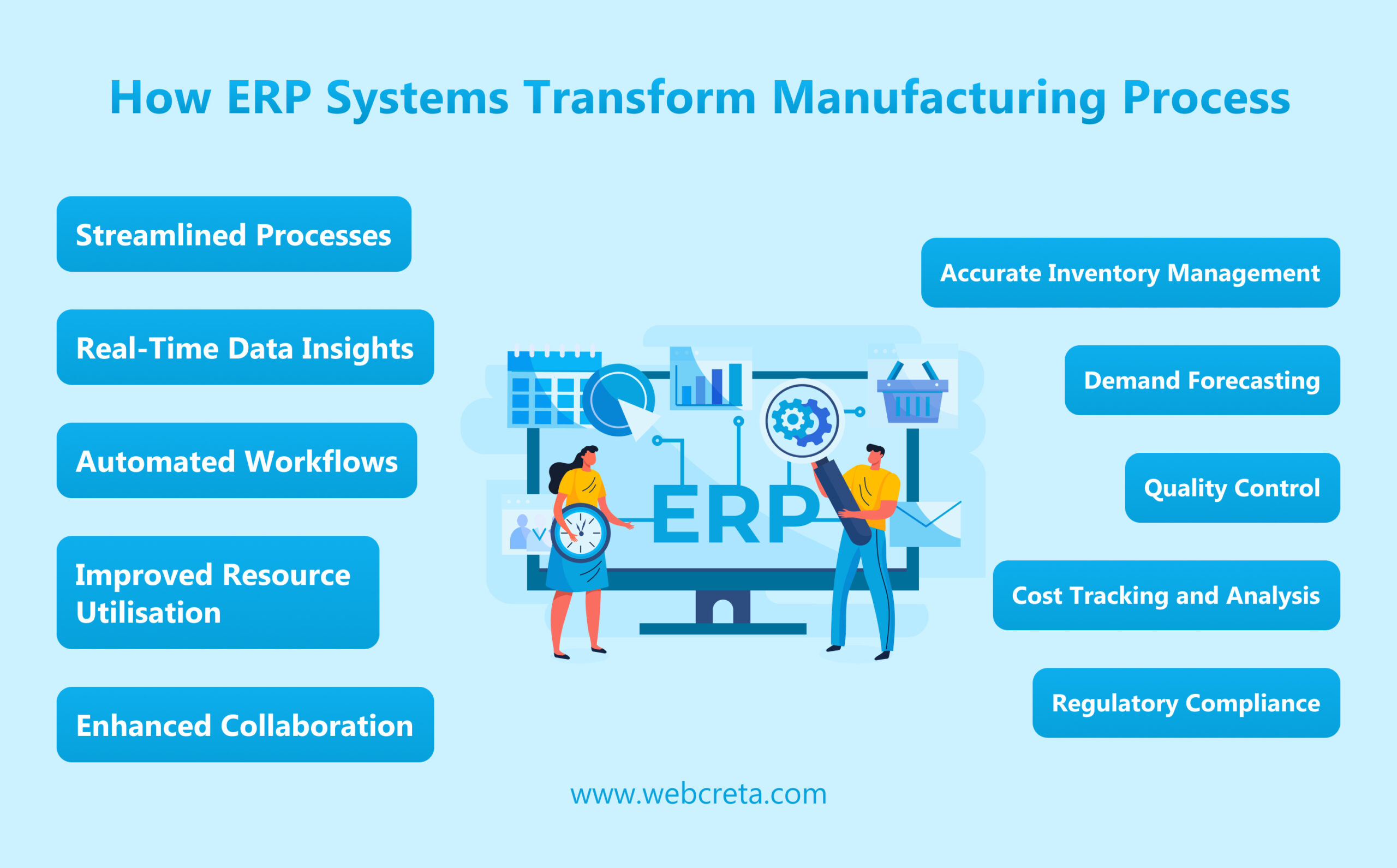
ERP systems are integrated software solutions that manage and automate business processes across various departments, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and, most importantly, production. By centralizing data and providing real-time visibility, ERP systems empower businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational performance. In the context of production, ERP systems offer a range of features that directly contribute to enhanced efficiency.
Key Features Contributing to Efficiency - Inventory Management: Real-time tracking of inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and overstocking.
- Production Planning: Optimizing production schedules based on demand forecasts and resource availability.
- Quality Control: Monitoring product quality throughout the production process, ensuring adherence to standards.
- Supply Chain Management: Streamlining communication and collaboration with suppliers, improving material flow.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights into production performance, identifying areas for improvement.
Benefits of ERP in Production
Implementing an ERP system in production leads to a multitude of benefits, directly impacting efficiency and profitability.
Improved Inventory Management
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing manufacturers to optimize stock levels and reduce carrying costs. This eliminates the risk of stockouts, which can disrupt production schedules and lead to lost sales. Conversely, it also prevents overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs.
Optimized Production Planning and Scheduling
With accurate demand forecasts and resource availability data, ERP systems enable manufacturers to create optimized production schedules. This ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, minimizing idle time and maximizing output. Furthermore, ERP systems can automatically adjust production schedules in response to unexpected events, such as equipment breakdowns or material shortages.
Enhanced Quality Control
ERP systems integrate quality control processes into the production workflow, allowing manufacturers to monitor product quality at every stage. This enables early detection of defects, preventing them from reaching the final product. By identifying the root causes of quality issues, manufacturers can implement corrective actions and improve overall product quality.
Streamlined Supply Chain Management
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers, improving material flow and reducing lead times. This ensures that materials are available when needed, preventing production delays. By integrating with supplier systems, ERP systems can automate purchase orders, track shipments, and manage supplier performance.
Data-Driven Decision Making
ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics on all aspects of the production process, empowering manufacturers to make informed decisions. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production output, cycle time, and defect rates. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and implement targeted interventions.
Examples of ERP Implementation in Production - A food processing company uses ERP to track raw materials from farm to table, ensuring product traceability and compliance with food safety regulations.
- An automotive manufacturer uses ERP to manage its complex supply chain, coordinating the delivery of thousands of parts from hundreds of suppliers.
- An electronics manufacturer uses ERP to optimize its production schedule, balancing demand fluctuations and resource constraints.
Factoid: Companies using ERP systems often see a 15-20% improvement in on-time delivery performance. FAQ About ERP Systems and Production Efficiency What is the biggest advantage of using an ERP system in production?
What is the biggest advantage of using an ERP system in production?
The biggest advantage is improved visibility and control over the entire production process, leading to better decision-making and increased efficiency.
How much does it cost to implement an ERP system?
The cost of implementing an ERP system varies depending on the size and complexity of the business, the specific features required, and the chosen vendor. It’s best to get quotes from several providers;
Is it difficult to learn how to use an ERP system?
While there is a learning curve, most ERP systems offer user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training programs. The key is to choose a system that is well-suited to the specific needs of the business and to provide adequate training to employees.
Can an ERP system help with regulatory compliance?
Yes, many ERP systems include features that help manufacturers comply with industry regulations, such as ISO standards and environmental regulations.
What are some common challenges of ERP implementation?
Common challenges include data migration, user adoption, and integration with existing systems. Proper planning and communication are essential for a successful implementation.
ERP systems are a valuable tool for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency in their production processes. By centralizing data, automating tasks, and providing real-time visibility, ERP systems empower businesses to optimize resource allocation, improve quality control, and streamline supply chain management. While implementation can be challenging, the benefits of ERP are significant, leading to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved profitability. Investing in an ERP system is a strategic decision that can help manufacturers gain a competitive edge in today’s demanding market.
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, operational efficiency is paramount. Companies are constantly seeking ways to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a powerful tool to achieve these goals, offering a comprehensive solution that integrates various aspects of the production cycle. This article explores how ERP systems contribute to enhanced efficiency in production processes, from raw material management to finished goods delivery.
ERP systems are integrated software solutions that manage and automate business processes across various departments, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and, most importantly, production. By centralizing data and providing real-time visibility, ERP systems empower businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational performance. In the context of production, ERP systems offer a range of features that directly contribute to enhanced efficiency.
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking of inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and overstocking.
- Production Planning: Optimizing production schedules based on demand forecasts and resource availability.
- Quality Control: Monitoring product quality throughout the production process, ensuring adherence to standards.
- Supply Chain Management: Streamlining communication and collaboration with suppliers, improving material flow.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights into production performance, identifying areas for improvement.
Implementing an ERP system in production leads to a multitude of benefits, directly impacting efficiency and profitability.
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing manufacturers to optimize stock levels and reduce carrying costs. This eliminates the risk of stockouts, which can disrupt production schedules and lead to lost sales. Conversely, it also prevents overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs.
With accurate demand forecasts and resource availability data, ERP systems enable manufacturers to create optimized production schedules. This ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, minimizing idle time and maximizing output. Furthermore, ERP systems can automatically adjust production schedules in response to unexpected events, such as equipment breakdowns or material shortages.
ERP systems integrate quality control processes into the production workflow, allowing manufacturers to monitor product quality at every stage. This enables early detection of defects, preventing them from reaching the final product. By identifying the root causes of quality issues, manufacturers can implement corrective actions and improve overall product quality.
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers, improving material flow and reducing lead times. This ensures that materials are available when needed, preventing production delays. By integrating with supplier systems, ERP systems can automate purchase orders, track shipments, and manage supplier performance.
ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics on all aspects of the production process, empowering manufacturers to make informed decisions. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production output, cycle time, and defect rates. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and implement targeted interventions.
- A food processing company uses ERP to track raw materials from farm to table, ensuring product traceability and compliance with food safety regulations.
- An automotive manufacturer uses ERP to manage its complex supply chain, coordinating the delivery of thousands of parts from hundreds of suppliers.
- An electronics manufacturer uses ERP to optimize its production schedule, balancing demand fluctuations and resource constraints.
The biggest advantage is improved visibility and control over the entire production process, leading to better decision-making and increased efficiency.
The cost of implementing an ERP system varies depending on the size and complexity of the business, the specific features required, and the chosen vendor. It’s best to get quotes from several providers.
While there is a learning curve, most ERP systems offer user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training programs. The key is to choose a system that is well-suited to the specific needs of the business and to provide adequate training to employees.
Yes, many ERP systems include features that help manufacturers comply with industry regulations, such as ISO standards and environmental regulations.
Common challenges include data migration, user adoption, and integration with existing systems. Proper planning and communication are essential for a successful implementation.
ERP systems are a valuable tool for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency in their production processes. By centralizing data, automating tasks, and providing real-time visibility, ERP systems empower businesses to optimize resource allocation, improve quality control, and streamline supply chain management. While implementation can be challenging, the benefits of ERP are significant, leading to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved profitability. Investing in an ERP system is a strategic decision that can help manufacturers gain a competitive edge in today’s demanding market.