Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the financial landscape. Its underlying technology, rooted in robust cryptography, provides a secure and transparent platform for digital transactions; This cryptographic foundation not only ensures the integrity of the Bitcoin network but also unlocks a range of benefits for users worldwide. Understanding these advantages is crucial for anyone looking to engage with or invest in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Understanding Bitcoin’s Cryptographic Foundation
Bitcoin’s security and functionality stem from several key cryptographic principles; These include:
- Hashing: Bitcoin uses cryptographic hash functions to create unique fingerprints of data, ensuring data integrity. Any alteration to the original data will result in a different hash, immediately revealing tampering.
- Digital Signatures: Transactions are digitally signed using private keys, allowing verification of the sender’s identity and preventing forgery.
- Public Key Cryptography: Bitcoin employs public and private key pairs. The public key is used to receive Bitcoin, while the private key is used to authorize transactions. This system ensures that only the owner of the private key can spend their Bitcoin.
The cryptographic underpinnings of Bitcoin offer several significant advantages:
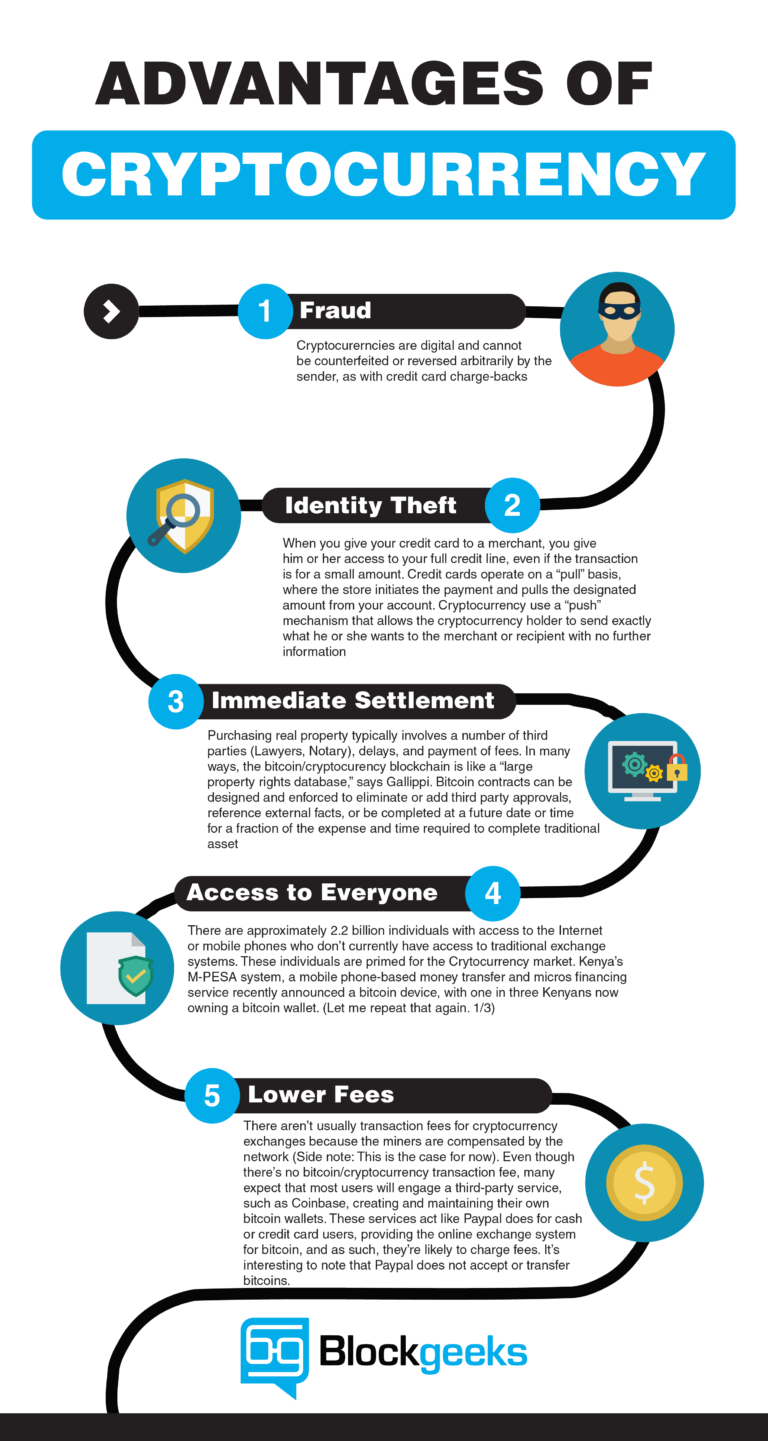
Enhanced Security
Cryptography provides a high level of security against fraud and unauthorized access. The use of digital signatures and hashing makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to tamper with transactions or steal Bitcoin.
Factoid: The Bitcoin network has never been successfully hacked in its history, a testament to the strength of its cryptographic security.
Transparency and Auditability
All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. While transactions are pseudonymous (not directly linked to real-world identities), they are fully transparent and auditable. This allows anyone to verify the validity of transactions and track the flow of Bitcoin.
Decentralization and Trustlessness
Bitcoin’s cryptography enables a decentralized system, meaning no single entity controls the network. This eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank, to process transactions. Instead, trust is built into the system through cryptographic verification.
Immutability
Once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or reversed. This immutability provides a high degree of certainty and prevents double-spending.
Reduced Counterparty Risk
Because Bitcoin transactions are peer-to-peer and verified cryptographically, they reduce the risk of relying on intermediaries. This can be particularly beneficial in situations where trust is limited or counterparty risk is high.
Practical Applications of Cryptographic Benefits
The benefits outlined above translate into various practical applications:
- Secure Online Payments: Bitcoin offers a secure alternative to traditional payment methods, especially for cross-border transactions.
- Protection Against Inflation: Bitcoin’s limited supply (21 million coins) can serve as a hedge against inflation, as its value is not subject to the control of central banks.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin can provide access to financial services for individuals who are unbanked or underbanked.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Bitcoin’s Cryptography
Q: Is Bitcoin completely anonymous?
A: No, Bitcoin is pseudonymous, not anonymous. Transactions are linked to public keys, not real-world identities. However, it is possible to link public keys to individuals through various means.
Q: Can Bitcoin transactions be reversed?
A: Once a transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, it is virtually impossible to reverse it. This is due to the cryptographic hashing and distributed nature of the network.
Q: Is Bitcoin’s cryptography foolproof?
A: While Bitcoin’s cryptography is very strong, it is not immune to all potential attacks. However, the network is constantly being monitored and updated to address any vulnerabilities.
Q: What is a Bitcoin wallet?
A: A Bitcoin wallet is a software or hardware device that stores your private keys and allows you to manage your Bitcoin. It enables you to send and receive Bitcoin transactions.
Q: How can I protect my Bitcoin private keys?
A: Protecting your private keys is crucial. Store them in a secure location, such as a hardware wallet or a paper wallet. Never share your private keys with anyone.
The Future of Bitcoin and Cryptography
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, Bitcoin’s cryptographic foundations will remain essential. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency, scalability, and privacy of Bitcoin’s cryptography. This includes exploring technologies like Schnorr signatures and Taproot, which promise to enhance the network’s capabilities.
Potential Future Developments
- Improved Scalability: Researchers are working on solutions to increase the number of transactions Bitcoin can process per second.
- Enhanced Privacy: New cryptographic techniques are being developed to further protect the privacy of Bitcoin users.
- Quantum Resistance: As quantum computing advances, efforts are underway to develop quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms for Bitcoin.
Bitcoin’s cryptography is the backbone of its security, transparency, and decentralization. By understanding the benefits of this cryptographic foundation, users can better appreciate the value and potential of Bitcoin as a digital currency and a revolutionary technology. As the technology evolves, the cryptographic underpinnings will continue to adapt and strengthen, ensuring Bitcoin’s long-term viability and its role in shaping the future of finance.