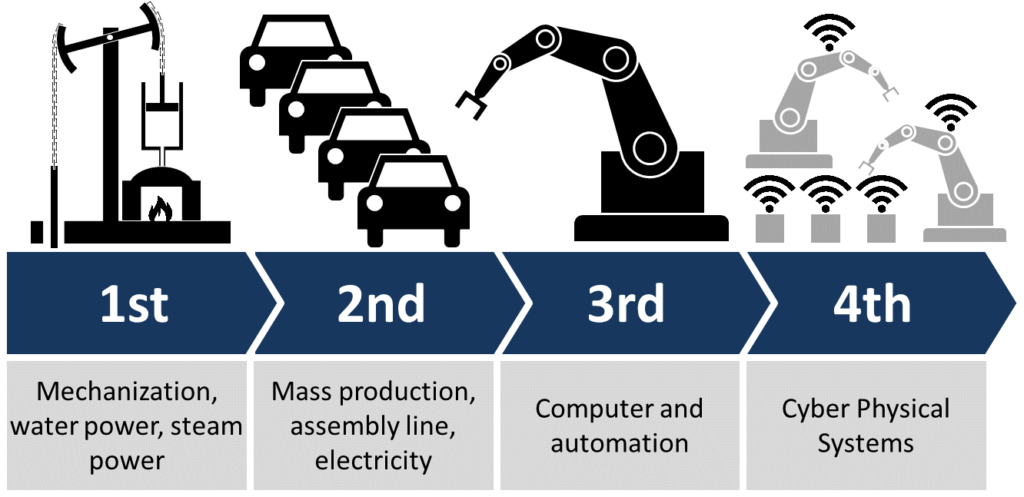
The world is undergoing a profound transformation‚ often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). This revolution builds upon the digital revolution‚ characterized by a fusion of technologies blurring the lines between the physical‚ digital‚ and biological spheres. It represents a fundamental shift in the way we live‚ work‚ and relate to one another‚ driven by unprecedented technological advancements. Understanding the key drivers and implications of this revolution is crucial for individuals‚ businesses‚ and governments alike to navigate the complexities of this rapidly evolving landscape.
Understanding the Core Concepts
Industry 4.0 is characterized by several key technological advancements that are converging to create a new industrial paradigm. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enabling machines to learn‚ adapt‚ and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices and systems to collect and exchange data‚ enabling real-time monitoring and control.
- Big Data and Analytics: Processing and analyzing massive amounts of data to extract insights and improve decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: Providing on-demand access to computing resources‚ enabling scalability and flexibility.
- Robotics and Automation: Automating tasks and processes to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs‚ enabling rapid prototyping and customization.
Key Technologies Driving the Revolution
The technologies listed above are not isolated entities. They are interconnected and interdependent‚ creating a synergistic effect that amplifies their individual impact. For example‚ AI algorithms can be used to analyze data collected by IoT devices‚ enabling predictive maintenance and optimized operations. Similarly‚ cloud computing provides the infrastructure necessary to store and process the vast amounts of data generated by these technologies.
The Impact on Various Sectors
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is impacting virtually every sector of the economy‚ from manufacturing and healthcare to transportation and agriculture. Businesses are adopting these technologies to improve efficiency‚ reduce costs‚ and create new products and services. Governments are investing in infrastructure and education to support the transition to a digital economy.
Factoid: The World Economic Forum estimates that Industry 4.0 could create $3.7 trillion in value by 2025.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the Fourth Industrial Revolution presents tremendous opportunities‚ it also poses significant challenges. These include:
- Job Displacement: Automation and AI may lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Skills Gap: Workers need to acquire new skills to adapt to the changing demands of the labor market.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The increased connectivity of devices and systems creates new vulnerabilities to cyberattacks.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of AI and other technologies raises ethical questions about privacy‚ bias‚ and accountability.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from governments‚ businesses‚ and individuals. Investing in education and training‚ developing robust cybersecurity measures‚ and establishing ethical guidelines are crucial for ensuring that the benefits of Industry 4.0 are shared broadly.
Preparing for the Future
To thrive in the age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution‚ individuals and organizations need to embrace lifelong learning‚ develop critical thinking skills‚ and cultivate adaptability. Businesses need to invest in digital transformation‚ foster innovation‚ and build agile organizational structures. Governments need to create a supportive regulatory environment‚ promote innovation‚ and invest in education and infrastructure.
The Role of Education and Training
Education and training are essential for preparing the workforce for the demands of Industry 4.0. This includes providing students with foundational skills in STEM (science‚ technology‚ engineering‚ and mathematics) fields‚ as well as developing skills in areas such as data analysis‚ AI‚ and cybersecurity. Lifelong learning programs are also crucial for helping workers adapt to changing job requirements.
FAQ — Frequently Asked Questions What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution‚ also known as Industry 4.0‚ is a new era characterized by the fusion of technologies blurring the lines between the physical‚ digital‚ and biological spheres. It builds upon the digital revolution and is driven by advancements in areas such as AI‚ IoT‚ big data‚ and robotics.
What are the key technologies driving Industry 4.0?
Key technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI)‚ Internet of Things (IoT)‚ Big Data and Analytics‚ Cloud Computing‚ Robotics and Automation‚ and Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing).
What are the potential benefits of Industry 4.0?
Potential benefits include increased efficiency‚ reduced costs‚ new products and services‚ improved decision-making‚ and greater innovation.
What are the challenges associated with Industry 4.0?
Challenges include job displacement‚ skills gap‚ cybersecurity risks‚ and ethical concerns.
How can businesses prepare for Industry 4.0?
Businesses can prepare by investing in digital transformation‚ fostering innovation‚ building agile organizational structures‚ and investing in employee training.
The world is undergoing a profound transformation‚ often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). This revolution builds upon the digital revolution‚ characterized by a fusion of technologies blurring the lines between the physical‚ digital‚ and biological spheres. It represents a fundamental shift in the way we live‚ work‚ and relate to one another‚ driven by unprecedented technological advancements. Understanding the key drivers and implications of this revolution is crucial for individuals‚ businesses‚ and governments alike to navigate the complexities of this rapidly evolving landscape.
Industry 4.0 is characterized by several key technological advancements that are converging to create a new industrial paradigm. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enabling machines to learn‚ adapt‚ and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices and systems to collect and exchange data‚ enabling real-time monitoring and control.
- Big Data and Analytics: Processing and analyzing massive amounts of data to extract insights and improve decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: Providing on-demand access to computing resources‚ enabling scalability and flexibility.
- Robotics and Automation: Automating tasks and processes to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs‚ enabling rapid prototyping and customization.
The technologies listed above are not isolated entities. They are interconnected and interdependent‚ creating a synergistic effect that amplifies their individual impact. For example‚ AI algorithms can be used to analyze data collected by IoT devices‚ enabling predictive maintenance and optimized operations. Similarly‚ cloud computing provides the infrastructure necessary to store and process the vast amounts of data generated by these technologies.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is impacting virtually every sector of the economy‚ from manufacturing and healthcare to transportation and agriculture. Businesses are adopting these technologies to improve efficiency‚ reduce costs‚ and create new products and services. Governments are investing in infrastructure and education to support the transition to a digital economy.
Factoid: The World Economic Forum estimates that Industry 4.0 could create $3.7 trillion in value by 2025.
While the Fourth Industrial Revolution presents tremendous opportunities‚ it also poses significant challenges. These include:
- Job Displacement: Automation and AI may lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Skills Gap: Workers need to acquire new skills to adapt to the changing demands of the labor market.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The increased connectivity of devices and systems creates new vulnerabilities to cyberattacks.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of AI and other technologies raises ethical questions about privacy‚ bias‚ and accountability.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from governments‚ businesses‚ and individuals. Investing in education and training‚ developing robust cybersecurity measures‚ and establishing ethical guidelines are crucial for ensuring that the benefits of Industry 4.0 are shared broadly.
To thrive in the age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution‚ individuals and organizations need to embrace lifelong learning‚ develop critical thinking skills‚ and cultivate adaptability. Businesses need to invest in digital transformation‚ foster innovation‚ and build agile organizational structures. Governments need to create a supportive regulatory environment‚ promote innovation‚ and invest in education and infrastructure.
Education and training are essential for preparing the workforce for the demands of Industry 4.0. This includes providing students with foundational skills in STEM (science‚ technology‚ engineering‚ and mathematics) fields‚ as well as developing skills in areas such as data analysis‚ AI‚ and cybersecurity. Lifelong learning programs are also crucial for helping workers adapt to changing job requirements.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution‚ also known as Industry 4.0‚ is a new era characterized by the fusion of technologies blurring the lines between the physical‚ digital‚ and biological spheres. It builds upon the digital revolution and is driven by advancements in areas such as AI‚ IoT‚ big data‚ and robotics.
Key technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI)‚ Internet of Things (IoT)‚ Big Data and Analytics‚ Cloud Computing‚ Robotics and Automation‚ and Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing).
Potential benefits include increased efficiency‚ reduced costs‚ new products and services‚ improved decision-making‚ and greater innovation.
Challenges include job displacement‚ skills gap‚ cybersecurity risks‚ and ethical concerns.
Businesses can prepare by investing in digital transformation‚ fostering innovation‚ building agile organizational structures‚ and investing in employee training.