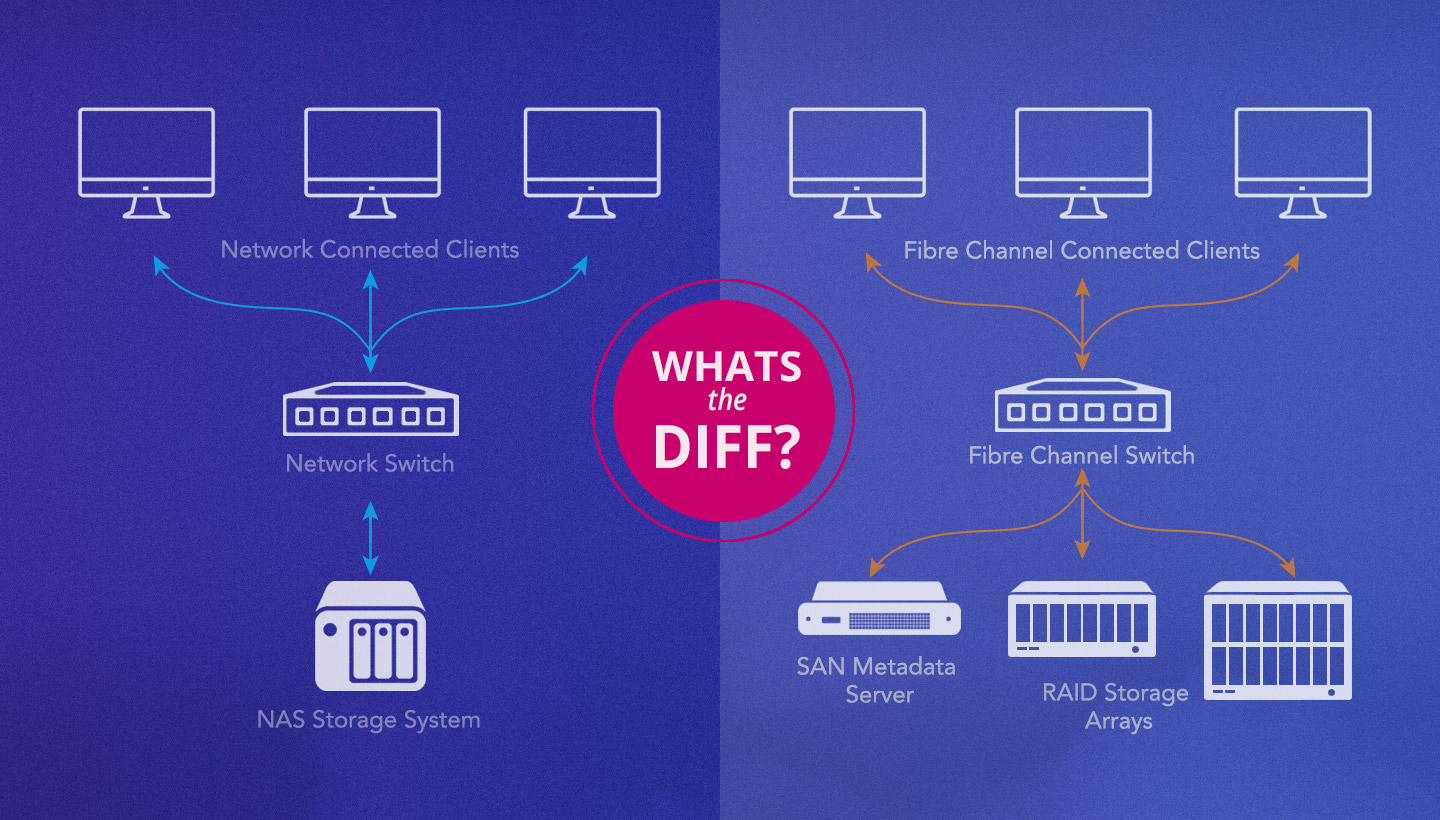
Choosing the right storage solution is a critical decision for any business, impacting everything from data accessibility to overall operational efficiency. Two prominent contenders in the storage arena are Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Networks (SAN). Understanding the nuances of each system is paramount to making an informed decision that aligns with your specific organizational needs and budgetary constraints. This article delves into the core differences between NAS and SAN, exploring their respective strengths and weaknesses to help you determine which is the better fit for your business.
Understanding Network Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS devices are essentially self-contained file servers that connect directly to your network. They provide file-level access, meaning clients request specific files, and the NAS device handles the file serving process. This makes NAS relatively easy to set up and manage, especially for smaller businesses with limited IT expertise.
Key Advantages of NAS:
- Ease of Use: Simple setup and management interface.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than SAN solutions.
- File Sharing: Excellent for centralized file storage and sharing across a network.
- Scalability: Can be scaled by adding more NAS devices to the network.
Potential Drawbacks of NAS:
- Performance Limitations: Performance can be limited by network bandwidth.
- Protocol Dependency: Relies on standard network protocols like TCP/IP.
- Single Point of Failure: A single NAS device failure can impact access to all files stored on it.
Exploring Storage Area Networks (SAN)
SANs, on the other hand, are dedicated, high-speed networks that provide block-level access to storage. This means clients have direct access to raw storage blocks, offering significantly faster performance and greater flexibility compared to NAS. SANs are typically used in enterprise environments where high performance and availability are critical.
Key Advantages of SAN:
- High Performance: Direct block-level access provides superior performance.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate large storage requirements.
- High Availability: Redundant components ensure high availability and data protection.
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of applications and operating systems.
Potential Drawbacks of SAN:
- Complexity: More complex to set up and manage than NAS.
- High Cost: Significantly more expensive than NAS solutions.
- Specialized Expertise: Requires specialized IT expertise for management and maintenance.
NAS vs SAN: A Comparative Table
| Feature | NAS | SAN |
|---|---|---|
| Access Method | File-Level | Block-Level |
| Performance | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Simpler | More Complex |
| Scalability | Good | Excellent |
The choice between NAS and SAN depends heavily on your specific requirements. If you need a simple, cost-effective solution for file sharing and centralized storage, NAS is likely the better option. However, if you require high performance, scalability, and availability for demanding applications, a SAN is the more appropriate choice. Consider factors such as budget, IT expertise, and performance needs when making your decision.
FAQ: NAS and SAN
Q: What is the main difference between NAS and SAN?
A: The main difference lies in the access method: NAS provides file-level access, while SAN provides block-level access.
Q: Which is more expensive, NAS or SAN?
A: SAN solutions are typically significantly more expensive than NAS solutions.
Q: Which is easier to manage, NAS or SAN?
A: NAS is generally easier to set up and manage than SAN.
Q: When should I choose NAS over SAN?
A: Choose NAS when you need a simple, cost-effective solution for file sharing and centralized storage.
Q: When should I choose SAN over NAS?
A: Choose SAN when you require high performance, scalability, and availability for demanding applications.
Ultimately, selecting the right storage solution involves careful consideration of your business needs and priorities. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both NAS and SAN will empower you to make an informed decision that optimizes your data storage infrastructure. The decision on whether to use NAS or SAN should be driven by the specific demands of your business, and it’s wise to consult with an IT professional to ensure the chosen solution aligns with your long-term goals.
Making the Right Choice: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the complex world of storage solutions can be daunting. To simplify the decision-making process, consider these steps:
- Assess Your Needs: Begin by thoroughly evaluating your current and projected storage requirements. How much data do you need to store? What are your performance expectations? What level of availability do you require?
- Evaluate Your Budget: Determine your budget for storage infrastructure. Remember to factor in not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, support, and potential upgrades.
- Consider Your IT Expertise: Assess the level of IT expertise available within your organization. If you have limited IT resources, a simpler solution like NAS may be more practical.
- Analyze Your Applications: Identify the applications that will be utilizing the storage solution. Some applications, such as databases and virtualization platforms, require high performance and are better suited for SAN environments.
- Explore Hybrid Solutions: Don’t be afraid to explore hybrid solutions that combine elements of both NAS and SAN. For example, you could use NAS for file sharing and SAN for critical applications.
- Consider Future Growth: Choose a solution that can scale to meet your future storage needs. Scalability is crucial for long-term investment protection.
Beyond NAS and SAN: Emerging Technologies
While NAS and SAN remain popular choices, several emerging technologies are also shaping the storage landscape. These include:
- Object Storage: Ideal for storing unstructured data, such as images, videos, and documents. Object storage offers excellent scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI): Combines compute, storage, and networking resources into a single, integrated system. HCI simplifies infrastructure management and improves resource utilization.
- Cloud Storage: Provides on-demand storage resources over the internet. Cloud storage offers flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
Seeking Expert Advice
Given the complexity of storage solutions, it’s often beneficial to seek expert advice from IT consultants or storage vendors. These professionals can help you assess your specific needs, evaluate different options, and design a storage infrastructure that meets your requirements and budget.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the optimal storage solution is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and competitiveness. By carefully evaluating your needs, considering your budget, and exploring available options, you can make an informed choice that empowers your organization to thrive in today’s data-driven world. Remember that the best storage solution isn’t necessarily the most expensive or the most technologically advanced; it’s the one that best aligns with your specific requirements and long-term goals. Therefore, take the time to do your research and choose wisely.